Simulation Education
What does 'low fidelity' aging simulation entail?
'Low fidelity' aging simulation offers a simple but effective way to experience the physical limitations and sensory challenges of aging. This form of simulation focuses on realistic scenarios that are accessible to different target groups, such as students and professionals. Through specially designed exercises, participants gain insight into what it feels like to live with, for example, limited mobility or poor vision. These simulations are not only accessible, but also flexible in use in educational and training programs. They form a valuable basis for empathy and awareness.
Practical examples of the use of OSP in schools and organizations
In education, OSPs are used to teach students how to interact with older patients and clients. For example, health care and social studies programs have integrated simulation programs into their curriculum to increase empathy and understanding. In professional settings, such as healthcare institutions and training organizations, these simulations are used to train staff in elderly communication and caregiving. These practical examples show that simulations not only improve skills, but also create a more inclusive attitude toward older people. This makes OSP a valuable tool in various sectors.
Expected learning objectives and effects of simulation sessions:
1 Increasing Empathy
The main goal of the sessions is to increase empathy and foster a deep understanding of the challenges of aging. By recreating the experience of aging, participants develop a greater understanding and respect for older adults and the obstacles they face on a daily basis.
2 Developing skills
Participants develop important skills such as reflection, communication and problem solving. These skills are tested in contexts that older adults experience in their daily lives, making participants better prepared to act caringly and effectively.
3 Creating awareness
The sessions contribute to a broader societal awareness of elderly care and inclusion. Participants change their attitudes and behavior in the long term, which not only benefits the elderly, but also society as a whole.
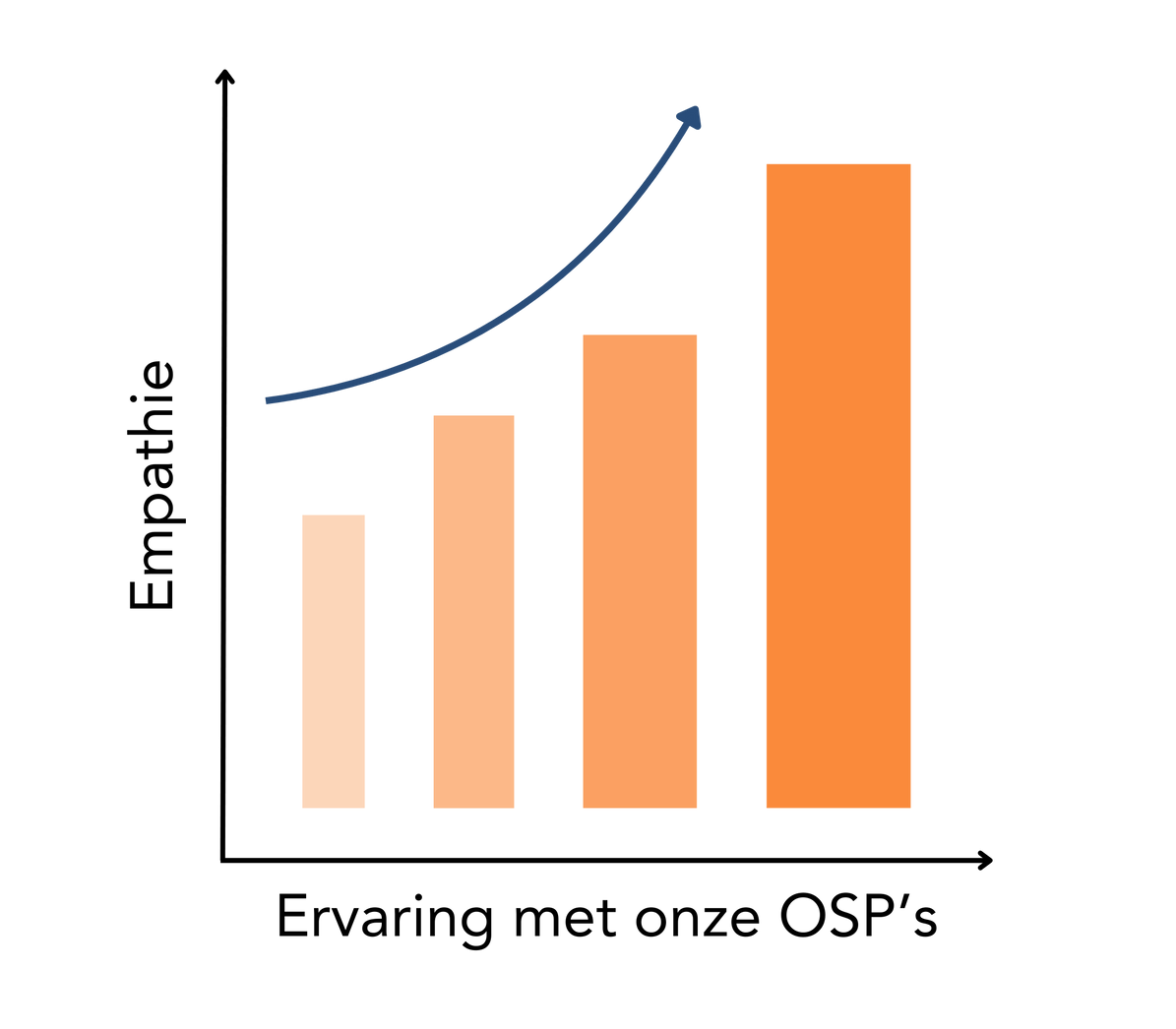
Scientific evidence for improving empathy through simulation
Research has shown that simulations such as OSPs have a significant impact on increasing empathy in participants. Studies show that participants are better able to relate to the challenges of older adults and apply this knowledge in their interactions. This makes simulation a powerful tool for education and training, especially in healthcare. In addition, these programs promote a deeper understanding of how physical and emotional limitations interact, allowing for a more holistic approach to elderly care.
Future perspective of simulation education
The role of simulations in education will only become more important in the future, partly due to the increasing ageing of the population. The use of OSPs can be further expanded with new technologies such as augmented reality and interactive simulations. This opens doors for blended learning methods in which theory and practice are seamlessly integrated. With a focus on empathy and inclusion, simulation education offers a sustainable answer to the challenges of a changing society. In this way, we prepare the next generations for an inclusive approach to the elderly.